Step 18: How to Monitor Your SEO Progress

After setting up your website for search engine ranking success, how can you tell whether you’re achieving results? Marketers need to know how to monitor their website rankings and SEO progress so they can keep doing what’s working and adjust what isn’t.
Your website goals are unique to your business. Still, there are some metrics that almost all sites need to pay attention to.
In this SEO tutorial step, you’ll learn to watch three types of key performance indicators (KPIs) that will help you monitor your SEO progress:
- How to watch your organic traffic
- How to monitor search engine rankings
- How to track conversions (transactions)
First Things First: Essential Tools
Search engine optimization requires data to base decisions on. In the real world, turnstiles count how many people visit an attraction, and cash register receipts show sales. On a website, the software tools that keep track of visitors, conversions, and other kinds of data are known as analytics.
Without analytics installed on your website, you’re really driving blind. Though analytics software packages can cost thousands of dollars per month, you’re in luck: the search engines provide reliable software for free.
- Google Analytics offers data tracking and lots of cool reporting options. It is powerful and highly customizable, yet GA’s dashboard design still allows non-technical people to use it.
- Google Search Console (formerly known as Webmaster Tools), a site owner’s indispensable friend, provides tools and reports you can’t get in GA. The Search Console also acts as a communication center between Google and you if something goes wrong with your site.
If you haven’t set these up yet, take a little detour from the SEO tutorial and follow our guide to Getting Started with Google Search Console & Google Analytics. (Note: Bing Webmaster Tools are also recommended, since they can give you a second opinion and additional data and tools.)
How to Monitor Organic Traffic to Your Website
It’s possible to know about the users coming to your website — not only how many people visit, but also general information about them. Geographic area, browser, device type, and what they do on your site (such as where they come from, what page they land on, how long they stay, and what they do during their visit) are all insightful.
This isn’t science fiction; it’s analytics.
Organic search traffic, the realm of SEO, includes all site visitors coming from a search engine except from paid ads.
Here you’ll learn how to look at organic traffic data using Google Analytics. We’ll show you some basics, but be sure to explore the many different menu options and data views available.
Who’s Visiting the Site from Organic Search?
From the left-hand menu in Google Analytics, choose Acquisition > Campaigns > Organic Keywords. By default, the data shows the number of sessions (visits) per keyword. However, since most keyword referrer data falls into the black hole labeled “(not provided)” for privacy reasons, you will get more useful information by clicking Landing Page as the primary dimension, as shown below.
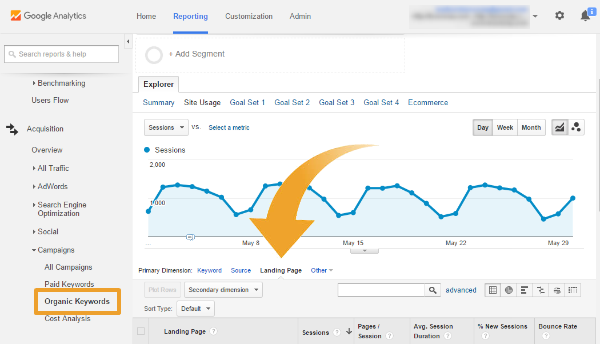
The data table below the graph, viewed by landing page as we suggest, shows you the website’s top-trafficked pages. The various columns tell you the visitors’ behavior on each page — how many bounce (i.e., leave the site after visiting only this page), how many complete a transaction, and how much conversion revenue was earned (more on conversion tracking later).

To monitor how your traffic changes over time, click the Compare to: check box in the upper right. Specify comparing to either the previous period (for instance, August vs. September), the previous year (such as March 2017 vs. March 2016), or a custom time period:
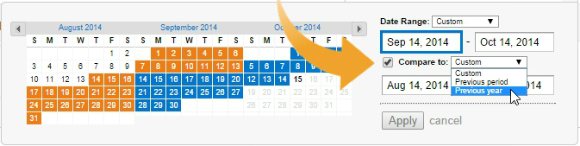
SEO Tip: A common mistake webmasters make is comparing month-to-month only. Since many businesses vary seasonally, an increase or decrease between consecutive months may indicate natural fluctuations more than SEO results.
Don’t forget to look at an entire year’s worth of data compared to the previous year, as well. That will show whether there’s been true SEO progress over time.
What Keywords Are Bringing Searchers to the Site?
As we mentioned, Google Analytics no longer reveals exact keyword referral data from secure searches. However, here’s a trick: If you have organized your website in silos (covered in Step 12) and focused each page’s content around a keyword topic (as discussed in lessons 6 and 7), you can look at the landing page data (shown above) and pretty well deduce what keywords are bringing people to your site.
Google Search Console does provide a little more keyword data. The data represents search queries run on Google only, which is limited but still useful. To see what keywords brought searchers to your site, log in to your Google Search Console account and choose Search Traffic > Search Analytics from the left-hand menu.
SEO Tip: In GSC, the Search Analytics data goes back only three months. It’s a good idea to download that data on a regular basis and store it in Excel or another spreadsheet program where you can track and analyze your Google keyword traffic.
How to Check Your Search Engine Rankings

Monitoring search engine rankings is important, but it’s not the best way to measure SEO success. It’s primarily useful as an early-warning metric, since rankings can move even before you’ve noticed traffic, revenue, or other real metrics changing. That’s because you won’t get much organic traffic from search unless your rankings are on Page 1 of the search engine results pages (SERPs).
Still, watching your organic rankings can sometimes reveal potential problems or, conversely, validate your optimization efforts.
For example, if your home page jumps from Page 10 up to Page 2 for a keyword, that ranking shift indicates that something — an algorithm change and/or your own efforts — worked in your favor. On the other hand, a drastic drop in search rankings can warn you of a problem with your site or indicate that you might have been penalized.
So Where Does Your Site Rank?
A few years ago, the same results would be returned no matter who searched for a query. It was a lot simpler then to monitor search engine rankings.
As we explained in Step 3, the search engines now personalize results — based on the searcher’s web history, physical location, Google+ circles, etc. — so that different people see different SERPs. You can try to de-personalize your results by 1) signing out of Google/Bing, 2) clearing your browser’s cache to remove web
history, and 3) changing your search settings to a general location such as “U.S.” But even if you go to all this trouble, your results will still reflect some customization.
Only unbiased results will let you compare apples to apples, and for that, you need tools. In fact, SEO is nearly impossible without good tools.
The SEOToolSet, which we developed to manage our own clients’ SEO projects, includes a Ranking Monitor to check a site’s search engine rankings. Our Ranking Monitor lets you compare your rankings over time for each of your keywords — across your choice of major search engine markets worldwide!
In other words, this automated tool keeps track of your SEO progress in saved reports so you can compare your rankings over time.
There’s no free version, but you get this SEO tool when you subscribe to the SEOToolSet! Priced way below other tools on the market at only $24.95/month, SEOToolSet also has a 30-day money back guarantee so you can try it risk-free. Here’s where you can learn more about Bruce Clay’s SEOToolSet.
How to Track Conversions
What do you want people to do on your website?
Each business has its own defined conversion goals — subscriptions, sales, sign-ups, donations, or other actions it wants site visitors to take. Ultimately, you’ll need to decide which specific metrics you need to watch to see how your
website is performing. These bottom-line metrics are really the most important indicators of your SEO progress.
In Google Analytics, you can set up conversion goals that can be measured. Choose Admin from the top navigation, and then click Goals in the right-hand column. You choose what should signal a conversion transaction (for example, when a user opens the checkout page, or sees the thank-you page).
You can set up goals at every step along your conversion path so you can see exactly where you’re losing people in your sales funnel. GA also lets you assign monetary values to conversion goals, enabling your analytics data to track the revenue per transaction, per page.
Setting up conversion goals is a multi-step process that varies depending on your particular hoped-for conversions. For more instructions, see Google Analytics Help for setting up goals.

An Essential Tool for SEO Maintenance
Our Single Page Analyzer tool helps you get “under the hood” of a web page and determine whether it’s correctly optimized, hitting keyword targets, having technical issues, or other.
Below is a free version of the most popular tool in our SEOToolSet. We include it here because we know you’ll need a way to analyze single pages as part of ongoing SEO maintenance. Your site changes over time, new pages go live, and many different hands (IT, content writers, etc.) touch your content. A content-analysis tool like this is essential for search engine optimization.
Enter a specific web page URL below and click Run Page Analyzer. Note that this free version of the SPA tool provides only a limited number of keywords. The full Single Page Analyzer in the SEOToolSet offers a more in-depth analysis.
SEO Tool: Single Page Analyzer
Now that you know how to watch your site traffic, monitor search engine rankings, and track conversion goals, you’re almost done with the tutorial! Click Next, because there’s one last thing you need to know …



